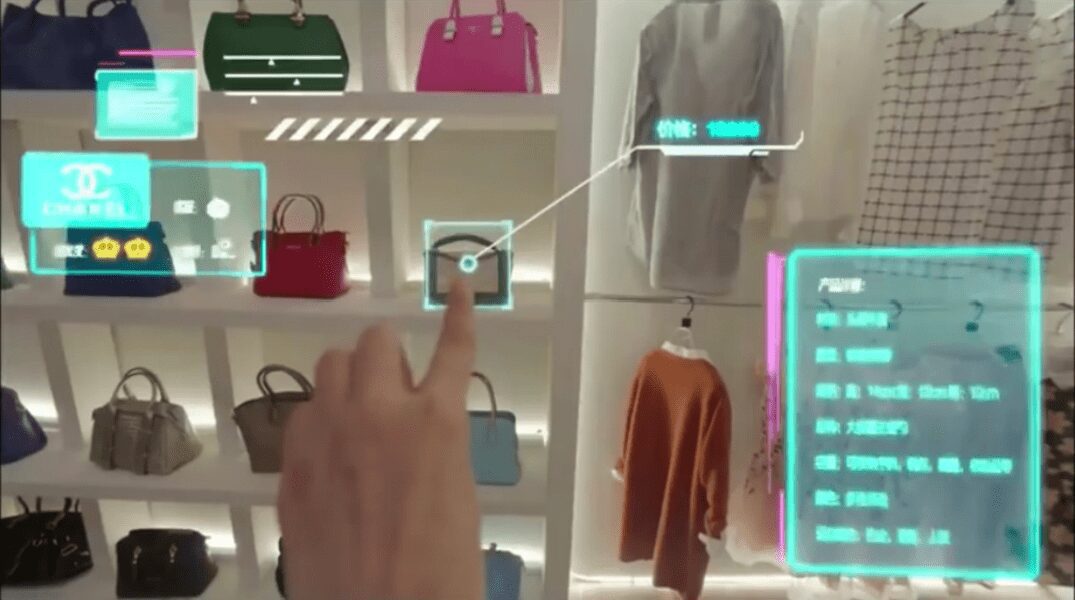
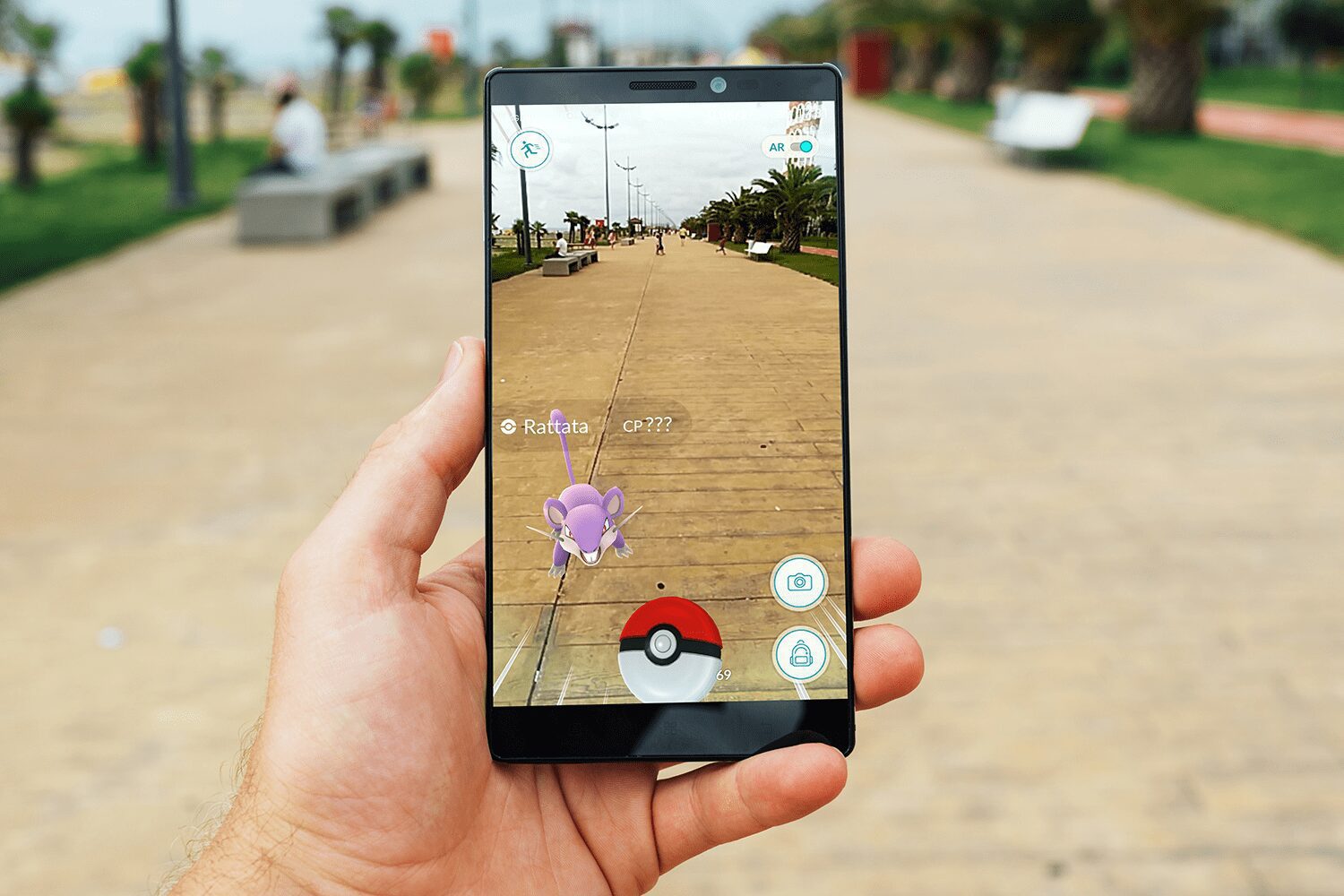
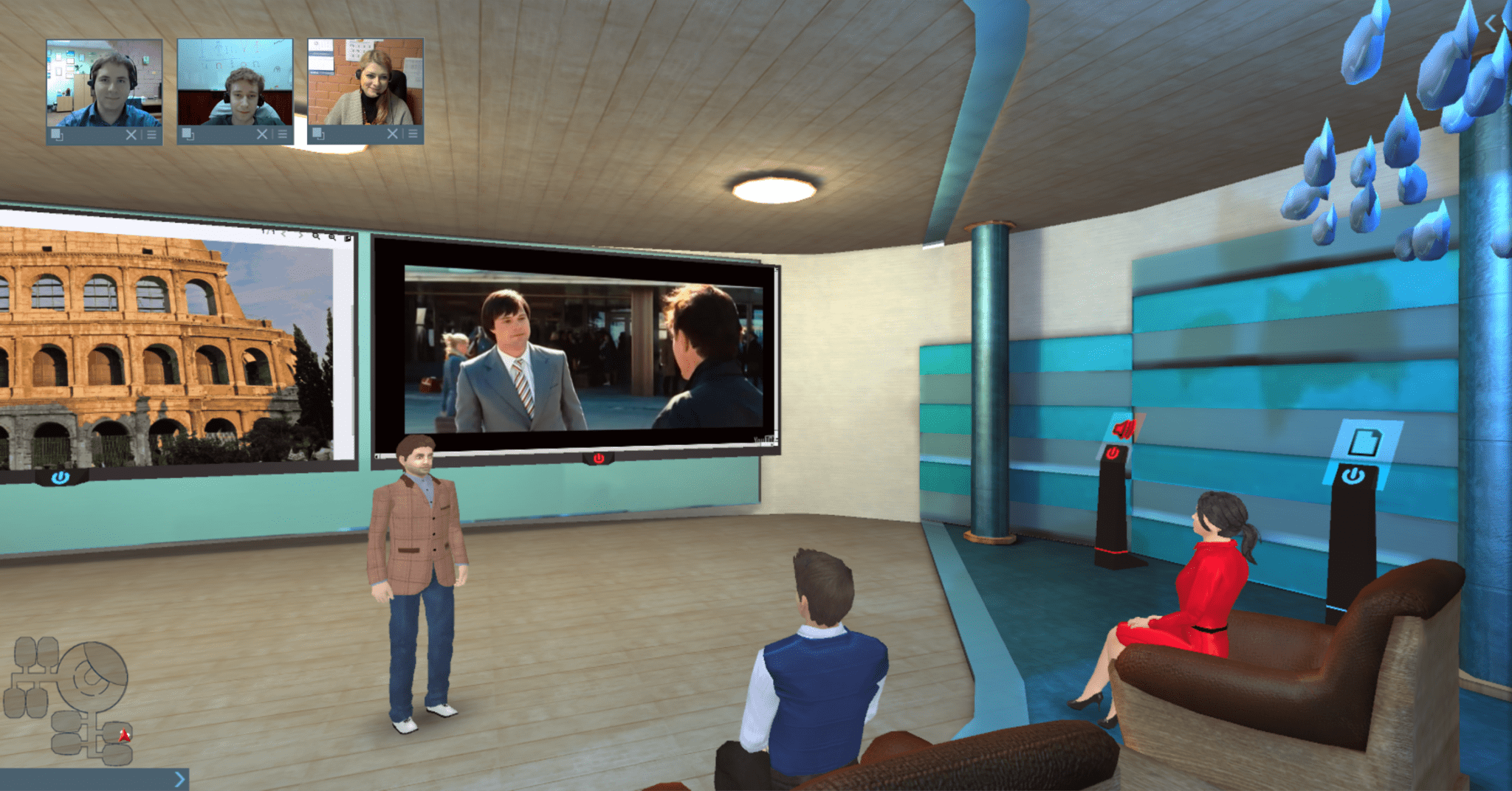
The competition among online retailers continues to grow, dramatically in light of the consequences of COVID-19. Capturing customer attention becomes more and more challenging, not to mention important. A wide range of choices and high customer service standards have made modern shoppers more demanding than ever. It means that getting ahead in the market is no longer just a matter of posting quality product photos. To stand out, online stores need to be creative and actively adopt innovation. In this context, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) show great promise in transforming the entire e-commerce industry.
In this blog post, we’ll explain why it’s high time to implement VR and AR into your e-commerce business. We’ll also discuss how these technologies can increase conversion rates and enhance the customer shopping experience.
Why e-commerce stores should adopt VR and AR now
Online shopping is on the rise today. Statistics show that e-commerce platforms are experiencing an unprecedented increase in traffic since the beginning of the year. The world’s most popular retail websites generated 21.96 billion visits in June 2020 compared to only 16.7 billion just a few months before, in January 2020.
The COVID-19 pandemic has, of course, played a crucial role in such a dramatic shift. Today, many people avoid shopping in physical stores because they want to minimize the health risks associated with the coronavirus.
For the same reason, customers are getting more accustomed to buying things in a few clicks instead of spending a lot of time visiting shopping malls. It shortens the buyer’s experience where they can purchase their products faster and with greater convenience.

However, the expectations of digital buyers are rising as well. People pay attention not only to what you sell but also to how you sell it. According to PWC’s research, 73 percent of customers said that shopping experience is a decision-making factor for them (along with product price and quality). Another study shows that most buyers believe that new technologies improve the purchasing process, both in real life and on the internet.

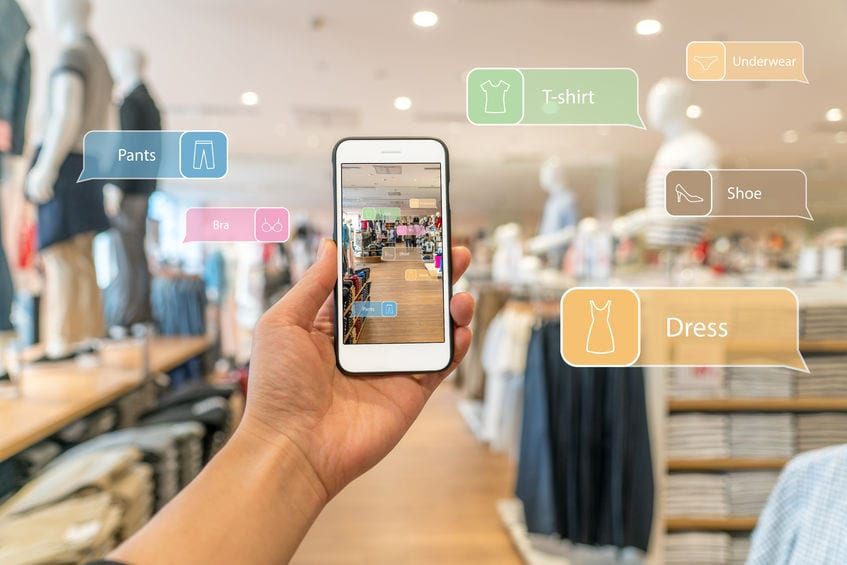
Finally, online shoppers love immersive experiences enabled by virtual reality and augmented reality. To give you some hard numbers, 61 percent of survey respondents pointed out that the AR technology has influenced their buying choices. In addition, the price for virtual reality headsets is going down. For example, you can buy Oculus Quest 2 for just $299. The availability and affordability of VR devices open the doors to a number of opportunities for VR-related shopping and user experience optimization.
Benefits of VR and AR for online retailers

Some online retailers hesitate to invest in VR and AR because they believe it’s just another passing user experience trend. However, this belief has few legs to stand on. In reality, VR and AR can completely reshape the way an e-commerce store functions, taking its KPIs to a new level. Here are the main advantages internet merchants can benefit from by adopting virtual and augmented reality.
Brand awareness
Building effective marketing campaigns is a challenge for any online business. Even if internet users see a company’s ad on Google or social media, odds are they’re unlikely to click on it, never mind being able to recall it in a few minutes. It’s not necessarily because the ad itself is bad. It’s because people are exposed to a huge amount of ‘digital noise’ these days.
In other words, people need a reason to remember a brand. Businesses that use VR and AR are more likely to stand out and get noticed as they offer a unique experience that internet users cannot get anywhere else.
Increased sales
To achieve success, e-commerce businesses can’t rely on only driving traffic to their websites. You need to engage and convince your potential customers. VR and AR experiences are two things; immersive and impressive. They make people want to engage with the virtual world. Just like when users play VR games, customers engaged with an online VR experience is more likely to stay on a web page or in an app for a longer time.
For online retailers, it means that visitors will view more products and make more purchases. Besides, the implementation of AR and VR is a great way to increase the number of returning customers who are loyal to your brand.
Reduced return rates
When buying things online, people cannot touch or experience a product. That’s why the risk that the customer makes a mistake and purchases something that doesn’t fit their needs is high. As a result, online retailers get many returns and spend a lot of resources on admin and managing these returns.
AR and VR give customers an opportunity to ‘feel’ a product and make sure that it’s exactly what they are looking for. By adopting these technologies, e-commerce stores can reduce the number of returns and save operational costs.
Benefits of VR and AR for online shoppers
The implementation of virtual and augmented reality is beneficial not only for e-commerce businesses but also for their customers. Many people choose to shop in brick and mortar stores because they don’t want to waste money on something that looks great on a photo but is completely different in real life. AR and VR experiences can significantly mitigate this fear. Let’s take a closer look at how virtual and augmented reality helps digital buyers make better shopping decisions.
Convenience
Since visiting a virtual store or showroom resembles real in-store experiences, it makes online shopping more convenient and anxiety-free. By moving around a fictitious environment, people can explore products similarly to how they would in a physical store, but from the comfort of their homes. Such simulations of real-life experiences allow customers to save a lot of time while enjoying most of the benefits offered by traditional shopping.
Try-before-you-buy
AR apps can cut down the time customers spend choosing the right item. For instance, users can just point their smartphone camera at their feet to see if a particular model of sneakers suit them.
Augmented reality also allows buyers to try things virtually, which is invaluable when you want to buy clothing or makeup. For example, customers can simply download an AR-enabled app to see if a particular lipstick shade looks good on them.

Satisfaction
People want to receive positive emotions when they spend time on the internet, and online shopping is no exception. In this context, good customer service is fundamental, however, it’s far from enough. Good customer service is a bare minimum that all customers expect when shopping online.
To get ahead of the curve, e-commerce businesses should pay a lot of attention to customer satisfaction and strive to not just meet but exceed buyers’ expectations. AR and VR are perfect tools to achieve this goal. Besides making shopping more convenient, these technologies can gamify the entire process of buying products online. Leading shoppers to not only wanting to purchase items but to return later, as they had an enjoyable time in the process.
VR and AR in e-commerce: success stories
According to the survey by Gartner, almost 50 percent of retailers plan to invest in augmented or virtual reality. While many are yet to make VR and AR a reality, there are still plenty who have made the transition. We’ve already seen many success stories about AR and VR implementation into e-commerce businesses. To inspire you for digital transformation and innovation, we’ve selected a few choice examples.
IKEA AR app
IKEA has an AR-based mobile application that allows users to see if a specific furniture item fits their room. The app shows all items at scale to give customers a sense of the products’ real dimensions. Users can also choose multiple items and place them in a room at once to make sure they look good together.
Sephora AR app
Sephora’s AR-enabled application was created to let users virtually try on makeup. First, the app scans a person’s face to figure out where the eyes, lips, and nose are. After that, users can choose different looks, for example, lip colors or lash styles, and see if the makeup suits them.

Since the first release of the Sephora AR app, a lot of brands have launched similar solutions. So, it becomes a real trend in the beauty industry. For instance, take a look at the prototype below. Such an app would allow you to try on different lipstick shades, eye and brow makeup, and even nail color.

Dior VR store
Dior’s VR store gives visitors an opportunity to virtually browse the collection of the brand’s soaps, lotions, etc. and buy their chosen products online. These VR retail experiences have helped the company adjust to lockdowns related to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, we would be very surprised if these changes aren’t here to stay.

Final thoughts
It’s hard to imagine the future of the e-commerce industry without the VR and AR experience.
Although the adoption level of these technologies among online retailers have yet to take off, the situation is expected to change in the near future. It means that you can reap all the benefits of implementing immersive experiences into your business before everyone else in the market does the same.