The “Internet of Things” (IoT) is the addition of internet connectivity and other sensors to physical objects. Broadband Internet becomes more widely available, the cost of connecting is decreasing, and more devices are being created with built-in network adapters. This movement creates a “perfect storm” for the IoT. That’s why IoT begins to move from ‘next big thing’ to something more and more of us are living with and it’s going to grow even more in coming years and eventually, most of us will use IoT technologies.
Gartner forecasts 21 billion connected things by 2020. That’s approximately four devices for every human being on the planet.
By 2020, more than half of major new business processes and systems will incorporate some element of the IoT. And we, as designers, should be ready for this moment. In this article, you’ll find everything you need to know about the increasingly connected world.
Where Can We Find IoT?
IoT isn’t just one group of devices, the term is used for a big range of connected tools, devices, and services. Technologies are infiltrating the everyday life and things around us are becoming smarter. Common categories of IoT today include:
- Connected home technology (these are products and services that make home life easier or more pleasant, such as smart thermostats, lighting, and energy monitoring)
- Wearables (such as activity/fitness trackers and smartwatches)
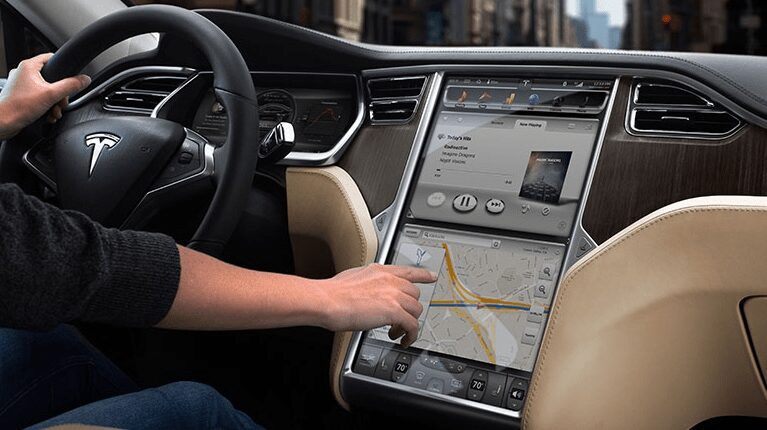
- Connected cars
- Urban systems (such as city rental bikes and parking meters/sensors)
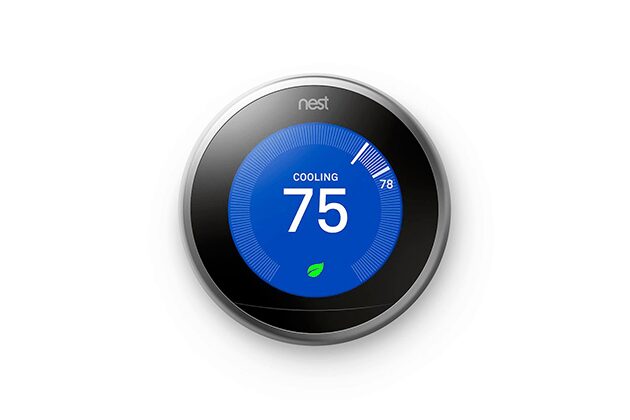
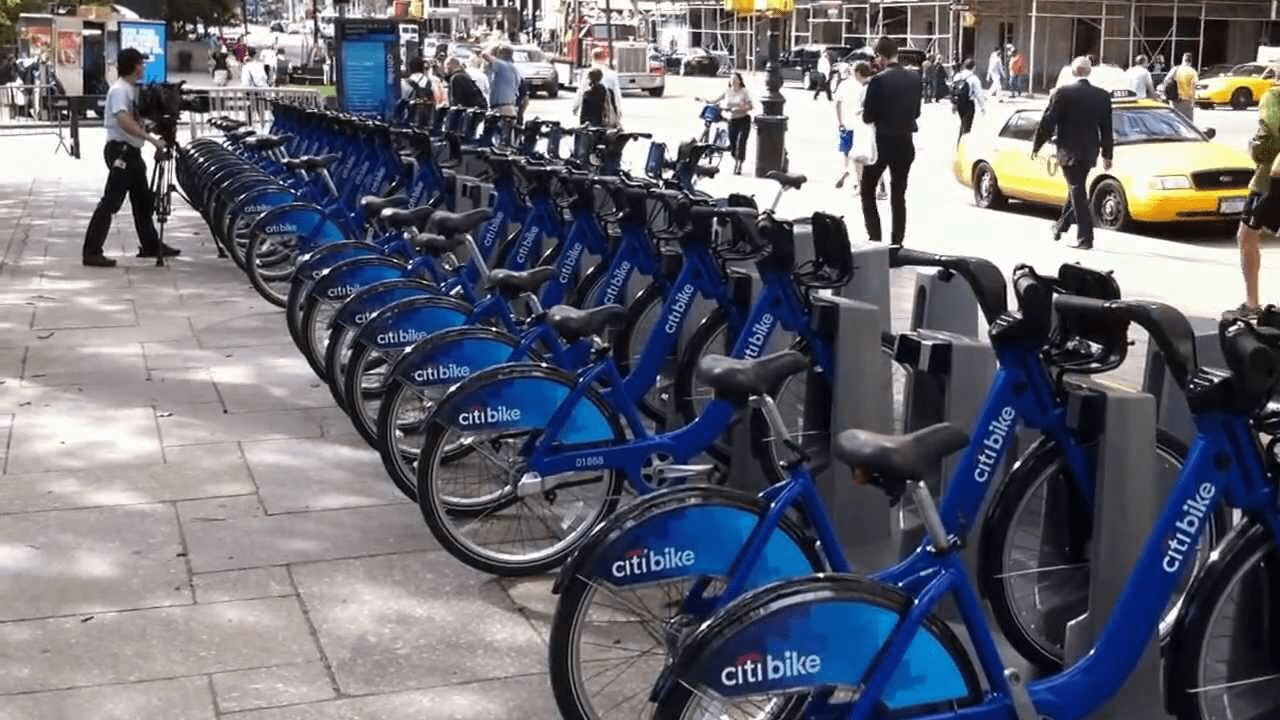



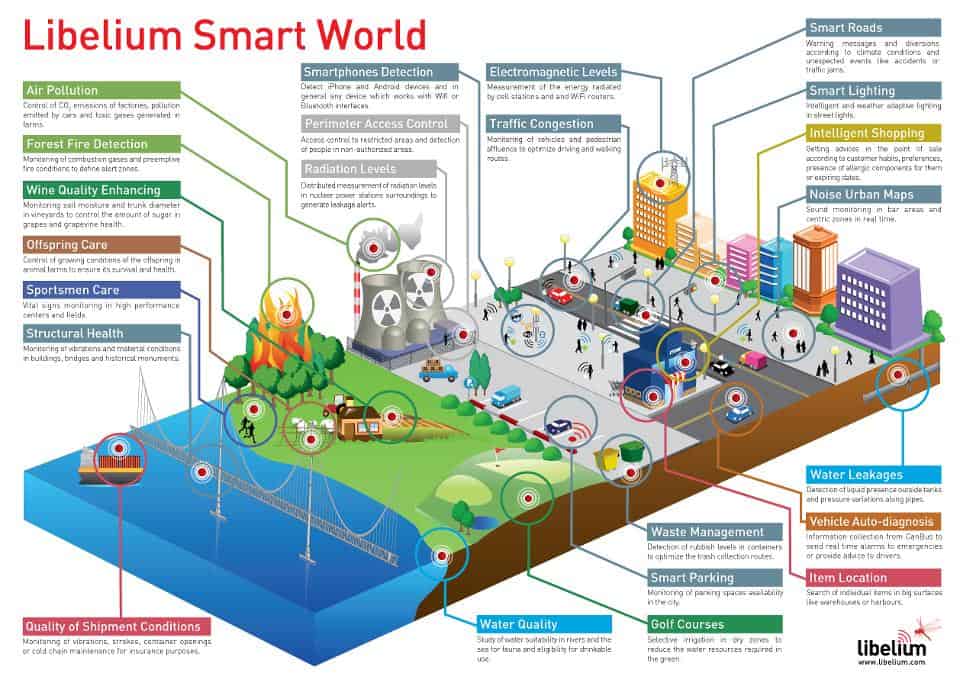
On a broader scale, the IoT can be used to create “smart cities” which can help us reduce waste and improve efficiency for our environments (e.g. energy use). Take a look at the visual below to see what something like that can look like.
5 Principles To Remember When Designing for IoT
Design is the critical component that bridges IoT technology’s potential with meeting real human needs. And it’s not surprise that IoT is a hot topic for designers today – it opens the door to a lot of opportunities but also to many challenges. While there are a huge array of things to consider while developing a IoT product, you’ll be more likely to gain traction if you keep following 5 principles in mind:
1. Design IoT Only If It Enhance User Experience
Just because something can be connected to the internet doesn’t mean it should be. IoT design requires a sharp focus on user needs because IOT products succeed only when they solve real problems and make users’ lives easier. Thus, if you want to connect something to the internet, you should have a clear answer on the question “Why do I want to do it?” User research should be a critical early step in any solid IoT UX project. Using insights gained from your research can help you explore the interaction contexts well before your team is burning hours designing or developing.
Making the ‘thing’ an IoT make sense only if it solves a real problem for the user. If connecting a product to the internet doesn’t enhance the experience, then don’t do it.
2. Create Good Onboarding
In the world of IoT getting your users up and running isn’t as simple as in a world of web or mobile apps. In addition to account creation, IoT devices usually require a proper configuration. Without a good onboarding experience, the setup phase might be really hard for the first-time users and there is a great possibility of user frustration or failure. That’s successful IoT product (like Nest) have set a relatively high bar for onboarding.
3. Prevent Glitching
Everyone experience occasional glitches in digital products. One common example is slow loading time on websites. Of course, it’s definitely frustrating when loading takes ages, but we are used to this. By contrast, we won’t expect real-world objects respond to us with glitches. When we turn off the lights in our room, we expect an immediate response. However, when we interact with a physical device over the internet (e.g. smart lighting system), that interaction might have the same latency issues as the website. So there’s the potential for delays in response. This could make the real world start to feel broken. Just imagine if you turned your lights off and they took two minutes to respond or failed to come on at all. As a designer, you should prevent all possible situations that can lead to glitch.
4. Make Sure It Works Locally
When designing for IoT, don’t assume always-on internet connectivity. In real life, IoT devices are often intermittently connected. Thus, it’s good to design for no internet connectivity at first, and see how much functionality can be done locally. Also, UX designers have to ensure that important functions (e.g. home security alarms for IoT Smart home system) continue to work properly when some devices go offline.
5. Design For Security and Data Privacy From the Outset
Security is a big issue. Recent high-profile hacks have raised the spectre of IoT-related security risks. More and more users are examining IoT devices for information about security. These consumers may be increasingly cautious about exposing personal information, especially when it is connected to physical spaces (such a local Wifi network) in their homes. Users might have questions like “Will someone be able to hack into my fridge and thereby get access to my entire network?” It’s your job, as a designer, to alleviate such fears. Always help users understand the security of your service by providing this information upfront.
Conclusion
A new generation of IoT is going to enhance our lives dramatically. We will spend less time on monotonous, boring tasks and will have more time to do what’s really important – like spending more time with our family or friends. I really hope the principles mentioned above help get your IoT effort aimed in the right direction.









![Bootstrap vs. Foundation Bootstrap vs. Foundation: Which Framework Should You Choose? [Infographic]](https://designmodo.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/bootstrap-vs-foundation.jpg)